New wave of infections delays economic recovery in Germany
The international economy seems bifurcated: While economies in East Asia and, to a lesser extent, major emerging economies such as India and Brazil continue to recover from the pandemic-related slump in spring, North America and large parts of Europe are expected to experience a weak winter. Particularly in Europe, a surge in infections and accompanying containment measures are likely to lead to declines in production. In early summer, the pandemic is expected to subside in the face of milder weather conditions in the northern hemisphere. This forecast assumes that the advanced economies will gradually succeed in bringing the pandemic under control with the use of vaccines in summer 2021. Production will then expand quite strongly in Europe and in the USA.
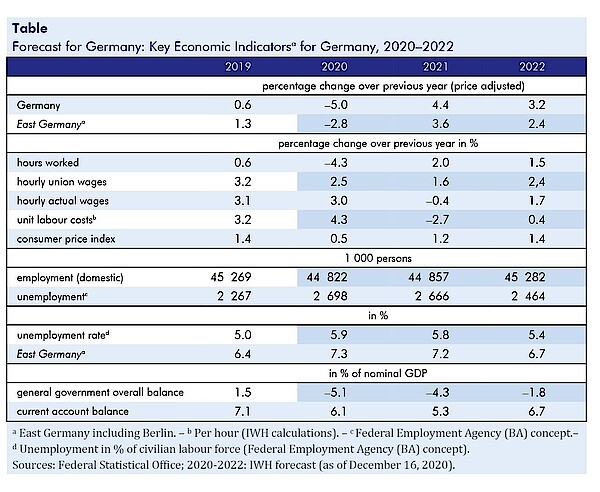
“The current lockdown in Germany will cause production to contract, albeit to a lesser extent than in spring since the decline is likely to be confined to parts of the services sector involving physical interaction,” says Oliver Holtemöller, head of the Department Macroeconomics and vice president at the IWH. By contrast, the manufacturing sector continues to benefit from a rebounding global economy. In the first quarter of 2021, positive effects from lifting restrictions will outweigh the drag from the expiration of the VAT (Value Added Tax) reduction. It is assumed that progressive vaccination of the population starting in summer 2021 will steadily reduce infections. The economy will then recover, supported by fairly strong growth rates in private consumption and investment. While employment has fallen more sharply since the start of the pandemic than during the financial crisis, it is projected to rise again from spring 2021. Consumer price inflation will remain moderate throughout the forecast period. The stability of real household incomes as well as the low number of corporate insolvencies are largely attributable to fiscal policy relief measures. The general government deficit ratio is expected to remain exceptionally high at 4.3% in 2021, after 5.1% in 2020.
According to Holtemöller, uncertainty about the efficacy of vaccinations to end the pandemic poses the main risk to the German economy. However, the current surge in infections throughout Europe also carries risks, such as the renewed faltering of demand from nearby European countries or supply chain disruptions. Supply chains could for example be compromised if illness or the closure of daycare centers and schools forces some workers to stay at home.
The extended version of the forecast (Neue Pandemiewelle verzögert konjunkturelle Erholung in Deutschland) contains the following four info boxes:
Box 1: Price developments of selected goods (in German)
Box 2: Estimation of potential output (in German)
Box 3: Financial assistance during the pandemic (in German)
Box 4: Collapse of travel services during the pandemic (in German)
Publication
Brautzsch, Hans-Ulrich; Claudio, João Carlos; Drygalla, Andrej; Exß, Franziska; Heinisch, Katja; Holtemöller, Oliver; Kämpfe, Martina; Lindner, Axel; Müller, Isabella; Schultz, Birgit; Staffa, Ruben; Wieschemeyer, Matthias; Zeddies, Götz: Neue Pandemiewelle verzögert konjunkturelle Erholung in Deutschland. IWH, Konjunktur aktuell, Jg. 8 (4), 2020. Halle (Saale) 2020.
Whom to contact
For Researchers

Vice President Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-800 Request per E-MailFor Journalists

Internal and External Communications
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-832 Request per E-MailIWH list of experts
The IWH list of experts provides an overview of IWH research topics and the researchers and scientists in these areas. The relevant experts for the topics listed there can be reached for questions as usual through the IWH Press Office.
Related Publications

Konjunktur aktuell: Neue Pandemiewelle verzögert konjunkturelle Erholung in Deutschland
in: Konjunktur aktuell, 4, 2020
Abstract
Während die Weltwirtschaft zweigeteilt ist – die Wirtschaft in Ostasien und in den großen Schwellenländern hat sich zügig erholt, für Nordamerika und Europa ist mit einem schwachen Winterhalbjahr zu rechnen –, lässt der Shutdown die Produktion in Deutschland zum Jahresende zurückgehen. Nach Lockerung der Infektionsschutzmaßnahmen, dank Impfkampagnen und milder Witterung dürfte die Erholung ab dem Frühjahr langsam wieder in Gang kommen. Im Jahr 2021 wird das BIP um 4,4% zunehmen, nach einem Rückgang um 5% im Jahr 2020. In Ostdeutschland fällt sowohl der Rückgang als auch der Wiederanstieg deutlich geringer aus.



