Joint Economic Forecast Spring 2025
Geopolitical turn intensifies crisis – structural reforms even more urgent
April 10, 2025

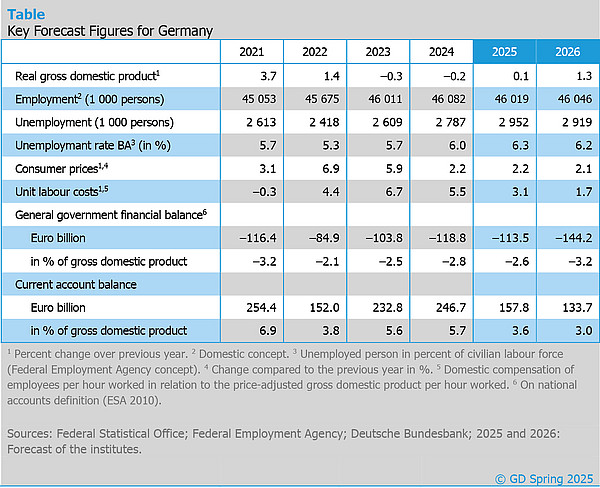
The German economy will continue to tread water in 2025. In their spring report, the leading economic research institutes forecast an increase in gross domestic product of just 0.1% for the current year. For 2026, the institutes expect gross domestic product to increase by 1.3%. In the short term, the new US trade policy and economic policy uncertainty are weighing on the German economy. The additional scope for public debt should gradually have an expansionary effect, but threatens to crowd out private consumption and private investment.
‘The geopolitical tensions and the protectionist trade policy of the USA are exacerbating the already tense economic situation in Germany,’ said Torsten Schmidt, Head of Economic Research at the RWI – Leibniz Institute for Economic Research. ‘In addition, German companies are facing increased international competition — especially from China. Last but not least, structural weaknesses such as the shortage of skilled labour and high bureaucratic hurdles are weighing on growth.’
The Bundestag and Bundesrat have amended the financial constitution to create additional scope for public debt — for defence, climate protection and infrastructure. However, it is unclear how the government's increased spending scope will be utilised. The institutes expect that hardly any additional funds will be called up for defence and investments this year. However, consolidation steps that would have been necessary without the change in the financial constitution will probably not be taken. For the coming year, the institutes expect additional expenditure of around 24 billion euros combined with an expansion impulse of around 0.5 percentage points for the gross domestic product. Smaller economic sectors are more likely to benefit from additional spending on defence and infrastructure. As these are already running at near full capacity, prices could continue to rise there.
The US tariffs on aluminium, steel and vehicle imports are likely to reduce GDP growth this year and next year by 0.1 percentage points each. The additional tariffs announced on 2nd April 2025 could double the negative effects. However, the specific effects are difficult to quantify, as tariff rates have never been raised so sharply in the world’s current globalised economy.
The situation on the labour market has deteriorated noticeably. Since mid-2022, the number of unemployed people has risen by 20%. That equates to more than 400,000 people. The unemployment rate has thus risen from 5.0% to 6.3%. Jobs are being lost mainly in manufacturing, construction and business services. At the same time, employment in the public sector, education and the healthcare sector continues to increase. The institutes expect unemployment to rise in the coming months. Unemployment is not expected to fall again until the economic situation improves over the course of 2026.
The phase of key interest rate cuts is likely to come to an end soon. In the USA, higher tariffs are jeopardising price stability. In the eurozone, a more expansive fiscal policy is causing capital market interest rates to rise, meaning that the key interest rate of 2.5% is not far from its neutral level. If the fiscal rules in the eurozone are loosened, the capital markets will become more important as a control body for sustainable public finances.
Germany is not only suffering from a weak economy, but above all has structural problems. These cannot be solved by simply increasing government spending and make reforms to boost potential output all the more urgent. For example, the social security system needs to be adapted to demographic change so that non-wage labour costs do not continue to rise sharply.
The Joint Economic Forecast was prepared by the ifo Institute – Leibniz Institute for Economic Research at the University of Munich in cooperation with the Austrian Institute of Economic Research (WIFO) Vienna, the Kiel Institute for the World Economy, Halle Institute for Economic Research (IWH) – Member of the Leibniz Association, and RWI – Leibniz Institute for Economic Research in cooperation with the Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna.
In East Germany, as in the west, the economy is in crisis
In 2024, the economy in East Germany shrank by 0.1% and in Germany as a whole by 0.2%. The IWH expects stagnation for East Germany in 2025 and growth of 1.1% in 2026. The unemployment rate is expected to be 7.8% in both 2025 and 2026, after 7.5% in 2024.
Our Expert

Vice President Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-800 Request per E-Mail


