New wave of infections suspends economic recovery
Global production has picked up again markedly following the dramatic slump last spring. The recovery is particularly pronounced in East Asia, where the pandemic is largely under control and the economy is benefiting from high global demand for industrial goods. In the euro area, however, GDP recently declined due to a new wave of infections, but the ongoing rollout of vaccines gives hope that the pandemic will come under control over the course of the year. Economic policy supports the recovery of the global economy. The comprehensive fiscal policy measures taken by the US government, together with a steep increase in commodity prices, have recently even given rise to inflation concerns. Economic activity, however, will not take place in lockstep across the world. While the strong economic momentum in China is already weakening again, the economy in the euro area is not expected to be in full swing until summer.
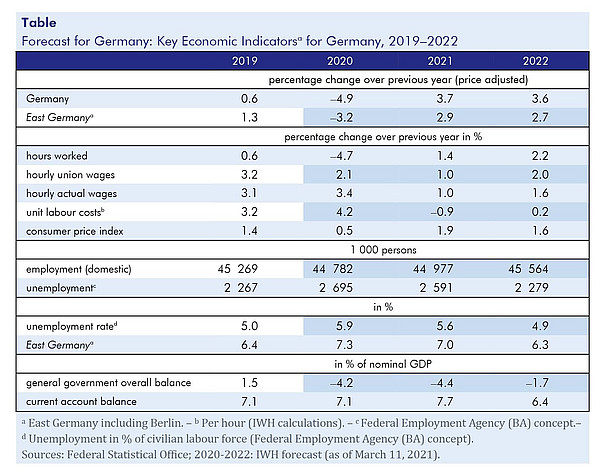
In Germany, the lockdown caused the service sector to contract at the end of 2020, while production increased markedly in industrial sectors and construction. Much of the personal services sector continues to be subject to restrictions, despite the relaxations approved in early March. Gross domestic product is expected to decline sizably in the first quarter of 2021. However, as the number of vaccinations increases, it is expected that the lockdown measures will be lifted successively. “Since overall disposable income has remained stable, also thanks to government support measures, a swift recovery in demand is probable,” says Oliver Holtemöller, head of the Department Macroeconomics and vice president at the IWH. The rebound of the global economy continues to benefit export-oriented manufacturing producers. The labour market is quite robust despite the second surge in infections, partly because short-time working schemes continue to exert a stabilising effect, says Holtemöller. Consumer prices will rise by 1.9% in 2021, significantly faster than in previous years, due to more expensive oil, the reversal of the temporary VAT cut, the introduction of nationwide emissions trading for CO2 pricing in the transport and heating sectors, and an increase in the minimum wage. The general government net lending/borrowing ratio in 2021 is expected to reach –4.4%, almost the same level as in the previous year.
According to Oliver Holtemöller, the central risk for the German and the global economy is still the uncertain course of the pandemic. It remains unclear for example whether existing vaccines are effective against all virus mutations. For Germany in particular, there is a risk that the recent easing of restrictions will trigger a third wave in infections, also because a comprehensive concept for the use of SARS-CoV-2 rapid tests is currently lacking. Effective enforcement of another lockdown seems socially hardly feasible. Certainly, however, the economic confidence of firms and households would suffer severely from another wave of infections.
The extended version of the forecast contains the following three info boxes:
Box 1: Assumptions and forecasts regarding the general conditions
(in German)
Box 2: Estimation of gross value added and gross domestic product
(in German)
Box 3: Estimation of production potential (in German)
Publication:
Brautzsch, Hans-Ulrich; Claudio, João Carlos; Drygalla, Andrej; Exß, Franziska; Heinisch, Katja; Holtemöller, Oliver; Kämpfe, Martina; Lindner, Axel; Müller, Isabella; Schultz, Birgit; Staffa, Ruben; Wieschemeyer, Matthias; Zeddies, Götz: Neue Infektionswelle unterbricht wirtschaftliche Erholung, in: IWH, Konjunktur aktuell, Jg. 9 (1), 2021. Halle (Saale) 2021.
Whom to contact
For Researchers

Vice President Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-800 Request per E-MailFor Journalists

Internal and External Communications
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-832 Request per E-MailIWH list of experts
The IWH list of experts provides an overview of IWH research topics and the researchers and scientists in these areas. The relevant experts for the topics listed there can be reached for questions as usual through the IWH Press Office.
Related Publications

Konjunktur aktuell: Neue Infektionswelle unterbricht wirtschaftliche Erholung
in: Konjunktur aktuell, 1, 2021
Abstract
Die globale Produktion hat nach dem dramatischen Einbruch vom vergangenen Frühjahr wieder deutlich zugelegt. Vor allem Ostasien erholt sich rasch, während das BIP im Euroraum zuletzt zurückging. Von Seiten der Wirtschafts politik sind die Bedingungen für eine Erholung der Weltwirtschaft insgesamt günstig. In Deutschland dürfte mit fortschreitender Impfkampagne und schrittweiser Aufhebung der Beschränkungen eine Normalisierung des Konsumverhaltens privater Haushalte die Konjunktur beflügeln. Im Jahr 2021 wird das BIP um 3,7% zunehmen, nach einem Rückgang um 4,9% im Jahr 2020. In Ostdeutschland fällt sowohl der Rückgang als auch der Wiederanstieg deutlich geringer aus.



