Productivity: More with Less by Better
Available resources are scarce. To sustain our society's income and living standards in a world with ecological and demographic change, we need to make smarter use of them.
Dossier

In a nutshell
Nobel Prize winners Paul Samuelson and William Nordhaus state in their classic economics textbook: Economics matters because resources are scarce. Indeed, productivity research is at the very heart of economics as it describes the efficiency with which these scarce resources are transformed into goods and services and, hence, into social wealth. If the consumption of resources is to be reduced, e. g., due to ecological reasons, our society’s present material living standards can only be maintained by productivity growth. The aging of our society and the induced scarcity of labour is a major future challenge. Without productivity growth a solution is hard to imagine. To understand the processes triggering productivity growth, a look at micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments is indispensable.
Our experts

Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-708 Request per E-Mail
President
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-700 Request per E-MailAll experts, press releases, publications and events on “Productivity”
Productivity is output in relation to input. While the concept of total factor productivity describes how efficiently labour, machinery, and all combined inputs are used, labour productivity describes value added (Gross Domestic Product, GDP) per worker and measures, in a macroeconomic sense, income per worker.
Productivity Growth on the Slowdown
Surprisingly, despite of massive use of technology and rushing digitisation, advances in productivity have been slowing down during the last decades. Labour productivity growth used to be much higher in the 1960s and 1970s than it is now. For the G7 countries, for example, annual growth rates of GDP per hour worked declined from about 4% in the early 1970s to about 2% in the 1980s and 1990s and then even fell to about 1% after 2010 (see figure 1).
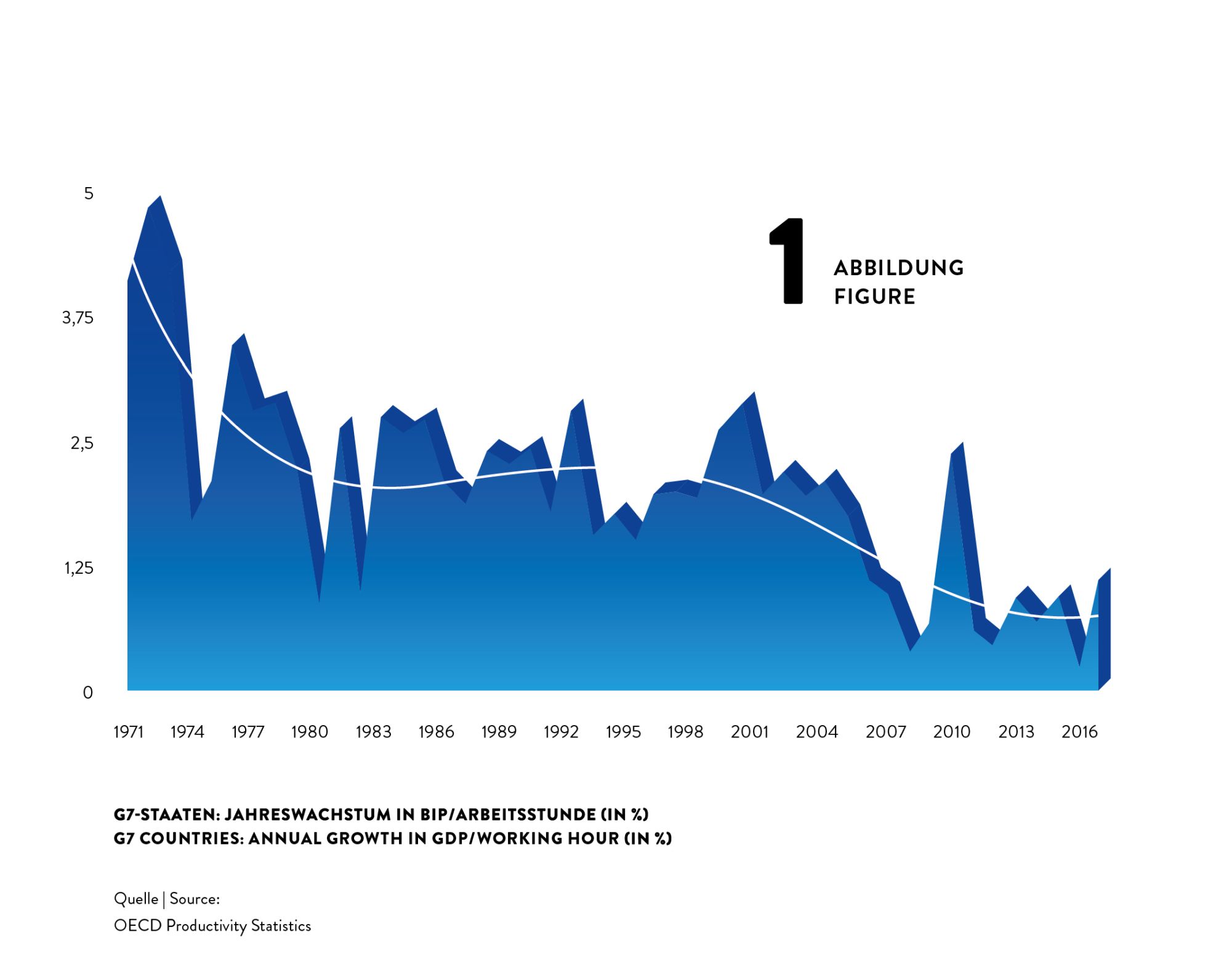
This implies a dramatic loss in potential income: Would the 4% productivity growth have been sustained over the four and a half decades from 1972 to 2017, G7 countries’ GDP per hour would now be unimaginable 2.5 times as high as it actually is. What a potential to, for instance, reduce poverty or to fund research on fundamentals topics as curing cancer or using fusion power!
So why has productivity growth declined dramatically although at the same time we see, for instance, a boom in new digital technologies that can be expected to increase productivity growth? For sure, part of the decline might be spurious and caused by mismeasurement of the contributions of digital technologies. For instance, it is inherently difficult to measure the value of a google search or another video on youtube. That being said, most observers agree that part of the slowdown is real.
Techno-Pessimists and Techno-Optimists
Techno-pessimists say, well, these new technologies are just not as consequential for productivity as, for instance, electrification or combustion engines have been. Techno-optimists argue that it can take many years until productivity effects of new technologies kick in, and it can come in multiple waves. New technology we have now may just be the tools to invent even more consequential innovations in the future.
While this strand of the discussion is concerned with the type of technology invented, others see the problem in that inventions nowadays may diffuse slowly from technological leaders to laggards creating a wedge between few superstar firms and the crowd (Akcigit et al., 2021). Increased market concentration and market power by superstar firms may reduce competitive pressure and the incentives to innovate.
Finally, reduced Schumpeterian business dynamism, i.e. a reduction in firm entry and exit as well as firm growth and decline, reflects a slowdown in the speed with which production factors are recombined to find their most productive match.
While the explanation for and the way out of the productivity puzzle are still unknown, it seems understood that using granular firm level data is the most promising path to find answers.
What are the Origins of Productivity Growth?
Aggregate productivity growth can originate from (i) a more efficient use of available inputs at the firm level as described above or (ii) from an improved allocation of resources between firms.
Higher efficiency at the firm level captures, e.g., the impact of innovations (Acemoglu et al., 2018) or improved firm organisation (management) (Heinz et al., 2020; Müller und Stegmaier, 2017), while improved factor allocation describes the degree of which scarce input factors are re-allocated from inefficient to efficient firms (‘Schumpeterian creative destruction’) (Aghion et al., 2015; Decker et al., 2021).
Most economic processes influence the productivity of existing firms and the growth and the use of resources of these firms and their competitors as well. The accelerated implementation of robotics in German plants (Deng et al., 2020), the foreign trade shocks induced by the rise of the Chinese economy (Bräuer et al., 2019), but also the COVID-19 pandemic, whose consequences are still to evaluate (Müller, 2021) not only effects on productivity and growth of the firms directly affected but at the same time may create new businesses and question existing firms.
While productivity can be measured at the level of aggregated sectors or economies, micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments are indispensable to study firm organisation, technology and innovation diffusion, superstar firms, market power, factor allocation and Schumpeterian business dynamism. The IWH adopts this micro approach within the EU Horizon 2020 project MICROPROD as well as with the CompNet research network.
As “creative destruction” may also negatively affect the persons involved (e. g., in the case of layoffs, Fackler et al., 2021), the IWH analyses the consequences of bankruptcies in its Bankruptcy Research Unit and looks at the implications of creative destruction for the society, e. g., within a project funded by Volkswagen Foundation searching for the economic origins of populism and in the framework of the Institute for Research on Social Cohesion.
Publications on “Productivity”

Political Influence and Financial Flexibility: Evidence from China
in: Journal of Banking and Finance, February 2019
Abstract
This paper investigates how political influence affects firms’ financial flexibility and speed of adjustment toward target leverage ratios. We find that at the macro level, firms in environments with high political advantages, proxied by provincial affiliations with heads of state as well as political status and party rank of provincial leaders, adjust faster. At the micro level, firms that are state-owned, have CPC members as executives, or bear low exposure to changes in political uncertainty adjust faster. When interacted, the micro-level political factors have more significant impact.

Produktion und Einkommen im Material Product System (MPS)
in: R. Mink, K. Voy (Hrsg.), Gesamtwirtschaftliche Einkommensbegriffe. Produktion und Einkommen im sozialpolitischen Kontext. Berliner Beiträge zu den volkswirtschaftlichen Gesamtrechnungen, Band 3. Marburg: Metropolis-Vertrag, 2019
Abstract
Der Beitrag behandelt die wirtschaftstheoretisch und sozioökonomisch bestimmten Besonderheiten der statistischen Erfassung von Entstehung, Verteilung und Umverteilung des Einkommens im Gesamtrechnungssystem der Zentralplanwirtschaften sowie deren Folgen für die wirtschaftspolitische Steuerung.

Regionale Wachstums- und Beschäftigungseffekte professioneller Fußballvereine – Eine europäische Analyse
in: Wirtschaft im Wandel, No. 5, 2018
Abstract
<p>Steigt ein Fußballverein ab, leiden die Fans. Leidet auch die Region? Der Beitrag nutzt abstiegsbedingte Änderungen in der räumlichen Verteilung der Vereine in vier großen europäischen Profifußballligen, um den kausalen Effekt des Abstiegs eines Erstligavereins auf das regionale Beschäftigungs- und Wirtschaftswachstum zu testen. Die Ergebnisse zeigen signifikant negative kurzfristige Effekte eines Abstiegs auf die Entwicklung der regionalen Beschäftigung und der Bruttowertschöpfung in sportbezogenen Wirtschaftszweigen. Darüber hinaus finden sich negative Auswirkungen auf das gesamte regionale Beschäftigungswachstum.</p>

Measuring the Impact of Household Innovation using Administrative Data
in: NBER Working Paper, No. 25259, 2018
Abstract
We link USPTO patent data to U.S. Census Bureau administrative records on individuals and firms. The combined dataset provides us with a directory of patenting household inventors as well as a time-series directory of self-employed businesses tied to household innovations. We describe the characteristics of household inventors by race, age, gender and U.S. origin, as well as the types of patented innovations pursued by these inventors. Business data allows us to highlight how patents shape the early life-cycle dynamics of nonemployer businesses. We find household innovators are disproportionately U.S. born, white and their age distribution has thicker tails relative to business innovators. Data shows there is a deficit of female and black inventors. Household inventors tend to work in consumer product areas compared to traditional business patents. While patented household innovations do not have the same impact of business innovations their uniqueness and impact remains surprisingly high. Back of the envelope calculations suggest patented household innovations granted between 2000 and 2011 might generate $5.0B in revenue (2000 dollars).

The Role of Auditors in Merger and Acquisition Completion Time
in: International Journal of Auditing, No. 3, 2018
Abstract
Using a sample of 664 merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions and office‐level audit data, this study investigates the role of auditors in M&A completion time. We find that having a common auditor for both acquirer and target firms in M&A transactions increases the completion time of such transactions because the exposure to higher litigation and reputational costs outweighs the information‐access advantage of common auditors. However, auditors' past experience in M&A transactions helps reduce completion time and costs. These results are robust to having Big N auditors at both ends as well as to various acquirer, target, and deal characteristics.



