Productivity: More with Less by Better
Available resources are scarce. To sustain our society's income and living standards in a world with ecological and demographic change, we need to make smarter use of them.
Dossier

In a nutshell
Nobel Prize winners Paul Samuelson and William Nordhaus state in their classic economics textbook: Economics matters because resources are scarce. Indeed, productivity research is at the very heart of economics as it describes the efficiency with which these scarce resources are transformed into goods and services and, hence, into social wealth. If the consumption of resources is to be reduced, e. g., due to ecological reasons, our society’s present material living standards can only be maintained by productivity growth. The aging of our society and the induced scarcity of labour is a major future challenge. Without productivity growth a solution is hard to imagine. To understand the processes triggering productivity growth, a look at micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments is indispensable.
Our experts

Department Head
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-708 Request per E-Mail
President
If you have any further questions please contact me.
+49 345 7753-700 Request per E-MailAll experts, press releases, publications and events on “Productivity”
Productivity is output in relation to input. While the concept of total factor productivity describes how efficiently labour, machinery, and all combined inputs are used, labour productivity describes value added (Gross Domestic Product, GDP) per worker and measures, in a macroeconomic sense, income per worker.
Productivity Growth on the Slowdown
Surprisingly, despite of massive use of technology and rushing digitisation, advances in productivity have been slowing down during the last decades. Labour productivity growth used to be much higher in the 1960s and 1970s than it is now. For the G7 countries, for example, annual growth rates of GDP per hour worked declined from about 4% in the early 1970s to about 2% in the 1980s and 1990s and then even fell to about 1% after 2010 (see figure 1).
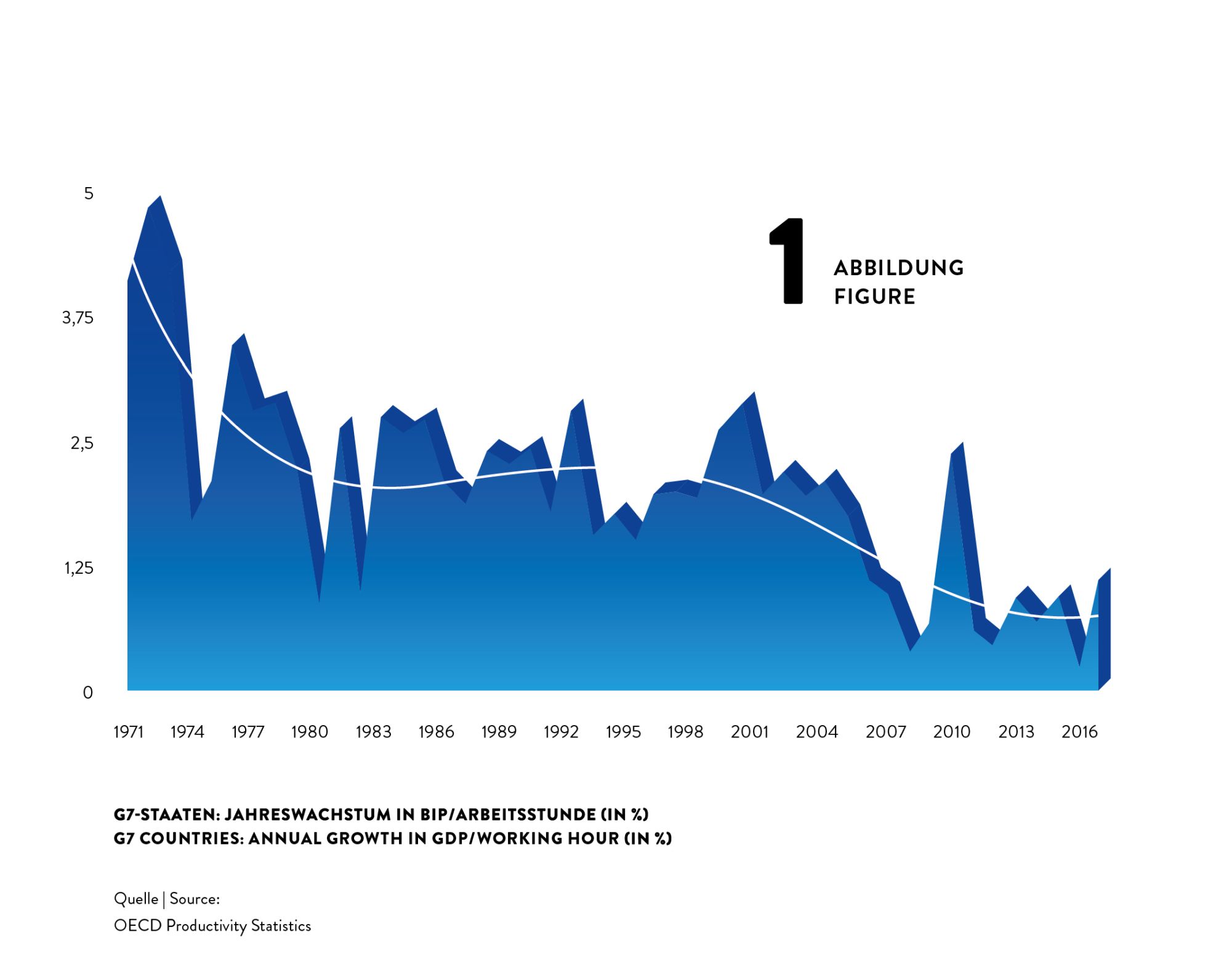
This implies a dramatic loss in potential income: Would the 4% productivity growth have been sustained over the four and a half decades from 1972 to 2017, G7 countries’ GDP per hour would now be unimaginable 2.5 times as high as it actually is. What a potential to, for instance, reduce poverty or to fund research on fundamentals topics as curing cancer or using fusion power!
So why has productivity growth declined dramatically although at the same time we see, for instance, a boom in new digital technologies that can be expected to increase productivity growth? For sure, part of the decline might be spurious and caused by mismeasurement of the contributions of digital technologies. For instance, it is inherently difficult to measure the value of a google search or another video on youtube. That being said, most observers agree that part of the slowdown is real.
Techno-Pessimists and Techno-Optimists
Techno-pessimists say, well, these new technologies are just not as consequential for productivity as, for instance, electrification or combustion engines have been. Techno-optimists argue that it can take many years until productivity effects of new technologies kick in, and it can come in multiple waves. New technology we have now may just be the tools to invent even more consequential innovations in the future.
While this strand of the discussion is concerned with the type of technology invented, others see the problem in that inventions nowadays may diffuse slowly from technological leaders to laggards creating a wedge between few superstar firms and the crowd (Akcigit et al., 2021). Increased market concentration and market power by superstar firms may reduce competitive pressure and the incentives to innovate.
Finally, reduced Schumpeterian business dynamism, i.e. a reduction in firm entry and exit as well as firm growth and decline, reflects a slowdown in the speed with which production factors are recombined to find their most productive match.
While the explanation for and the way out of the productivity puzzle are still unknown, it seems understood that using granular firm level data is the most promising path to find answers.
What are the Origins of Productivity Growth?
Aggregate productivity growth can originate from (i) a more efficient use of available inputs at the firm level as described above or (ii) from an improved allocation of resources between firms.
Higher efficiency at the firm level captures, e.g., the impact of innovations (Acemoglu et al., 2018) or improved firm organisation (management) (Heinz et al., 2020; Müller und Stegmaier, 2017), while improved factor allocation describes the degree of which scarce input factors are re-allocated from inefficient to efficient firms (‘Schumpeterian creative destruction’) (Aghion et al., 2015; Decker et al., 2021).
Most economic processes influence the productivity of existing firms and the growth and the use of resources of these firms and their competitors as well. The accelerated implementation of robotics in German plants (Deng et al., 2020), the foreign trade shocks induced by the rise of the Chinese economy (Bräuer et al., 2019), but also the COVID-19 pandemic, whose consequences are still to evaluate (Müller, 2021) not only effects on productivity and growth of the firms directly affected but at the same time may create new businesses and question existing firms.
While productivity can be measured at the level of aggregated sectors or economies, micro data on the level of individual firms or establishments are indispensable to study firm organisation, technology and innovation diffusion, superstar firms, market power, factor allocation and Schumpeterian business dynamism. The IWH adopts this micro approach within the EU Horizon 2020 project MICROPROD as well as with the CompNet research network.
As “creative destruction” may also negatively affect the persons involved (e. g., in the case of layoffs, Fackler et al., 2021), the IWH analyses the consequences of bankruptcies in its Bankruptcy Research Unit and looks at the implications of creative destruction for the society, e. g., within a project funded by Volkswagen Foundation searching for the economic origins of populism and in the framework of the Institute for Research on Social Cohesion.
Publications on “Productivity”

Searching where Ideas Are Harder to Find – The Productivity Slowdown as a Result of Firms Hindering Disruptive Innovation
in: IWH Discussion Papers, No. 22, 2023
Abstract
This paper proposes to explain the productivity growth slowdown with the poaching of disruptive inventors by firms these inventors threaten with their research. I build an endogenous growth model with incremental and disruptive innovation and an inventor labor market where this defensive poaching takes place. Incremental firms poach more as they grow, which lowers the probability of disruption and makes large incremental firms even more prevalent. I perform an event study around disruptive innovations to confirm the main features of the model: Disruptions increase future research productivity, hurt incumbent inventors and raise the probability of future disruption. Without disruption, technology classes slowly trend even further towards incrementalism. I calibrate the model to the global patent landscape in 1990 and show that the model predicts 52% of the decline of disruptive innovation until 2010.

Declining Job Reallocation in Europe: The Role of Shocks, Market Power, and Technology
in: IWH Discussion Papers, No. 19, 2023
Abstract
<p>We study changes in job reallocation in Europe after 2000 using novel microaggregated data that we collected for 19 European countries. In all countries, we document broad-based declines in job reallocation rates that concern most economic sectors and size classes. These declines are mainly driven by dynamics within sectors, size, and age classes rather than by compositional changes. Simultaneously, employment shares of young firms decline. Consistent with US evidence, firms’ employment has become less responsive to productivity shocks. However, the dispersion of firms’ productivity shocks has decreased too. To enhance our understanding of these patterns, we derive and apply a firm-level framework that relates changes in firms’ market power, labor market imperfections, and production technology to firms’ responsiveness and job reallocation. Using German firm-level data, we find that changes in markups and labor output elasticities, rather than adjustment costs, are key in rationalizing declining responsiveness.</p>

Declining Business Dynamism in Europe: The Role of Shocks, Market Power, and Technology
in: IWH-CompNet Discussion Papers, No. 2, 2023
Abstract
We study changes in business dynamism in Europe after 2000 using novel micro-aggregated data that we collected for 19 European countries. In all countries, we document a broad-based decline in job reallocation rates that concerns most economic sectors and size classes. This decline is mainly driven by dynamics within sectors, size, and age classes rather than by compositional changes. Large and mature firms experience the strongest decline in job reallocation rates. Simultaneously, the employment shares of young firms decline. Consistent with US evidence, firms’ employment has become less responsive to productivity shocks. However, the dispersion of firms’ productivity shocks has decreased too. To enhance our understanding of these patterns, we derive and apply a novel firm-level framework that relates changes in firms’ sales, market power, wages, and production technology to firms’ responsiveness and job reallocation.

Committing to Grow: Employment Targets and Firm Dynamics
in: IWH Discussion Papers, No. 17, 2023
Abstract
<p>We examine effects of government-imposed employment targets on firm behavior. Theoretically, such policies create “polarization,“ causing low-productivity firms to exit the market while others temporarily distort their employment upward. Dynamically, firms are incentivized to improve productivity to meet targets. Using novel data from East German firms post-privatization, we find that firms with binding employment targets experienced 25% higher annual employment growth, a 1.1% higher annual exit probability, and 10% higher annual productivity growth over the target period. Structural estimates reveal substantial misallocation of labor across firms and that subsidizing productivity growth would yield twice the long term increases in employment.</p>

Import Competition and Firm Productivity: Evidence from German Manufacturing
in: World Economy, No. 8, 2023
Abstract
Abstract We study how different types of import competition affect firm productivity using firm-product data from German manufacturing (2000-2014). Competition from high-income countries causes affected domestic firms to increase their productivity and lower their prices. Oppositely, import competition from low-wage countries does not lead to firm productivity gains. Instead, domestic firms' sales and input usage decline. Our findings confirm the intuition of ladder models that the effect of competition depends on the "closeness" of competitors. They are in line with widespread X-inefficiencies throughout the economy, which firms reduce in response to competition from high-income countries.



